 |
|
Aluminum Die Cast Parts comply with REACH and the EU RoHS 3 standards Other Die Casting Alloy Materials Comparison
A list of die casting surface treatments or surface coatings for die casting parts would include E-coat, powder coating, PVD, Hard anodize, Chem-Film or Alodine, Chromate, wet paint, zinc plate coating or galvanizing.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PURPOSE | ALUMINUM | ZINC | ZA |
| Decorative
finish |
Polish/Epoxy Plate Powder coat |
Plate Chromate Phosphate |
Plate (ZA-8, ZA-12) Chromate Phosphate |
| Environmental
or galvanic corrosion barrier |
Chromate Anodize Iridite |
Chromate Anodize Iridite |
Chromate Anodize Iridite |
| Fill and seal
surface and subsurface |
|||
| Improve wear
resistance |
- NADCA Product Standards for Die Casting
- NADCA Standards Alloy Data Sheets
- NADCA Standards for Quality
- NADCA Standards for Quality - Additional Information
Die Casting Description, Why Use Die Casting in aluminum:
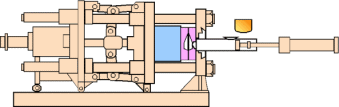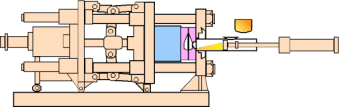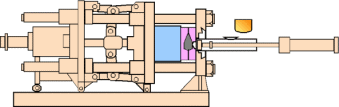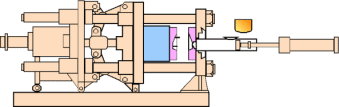
Aluminum Die Casting Manufacturing Compared to:
Forgings
Compared with forgings, die casting can be more complex in shape and
have shapes not forgeable, can have thinner sections, be held to closer
dimensions, and have coring not feasible in forging.
Plastic Injection moldings
Compared with plastic injection moldings, die casting are stronger,
stiffer, more stable dimensionally, more heat resistant, and are far
superior to plastics on a properties/coat basis. They help prevent
radio frequency and electromagnetic emissions. For chrome plating, die
castings are much superior to plastics. Die castings have a high degree
permanence under load compared to plastics, are completely resistant to
ultra-violet rays, weathering, and stress-cracking in the presence of
various reagents. Manufacturing cycles for producing die castings
are much faster than for injection moldings.
Extrusions
Compared to extrusions, die casting can be produced faster and more
net shape. Features and depressions on the sides, tops and bottoms can
be created in one operation. There is less waste using die casting than
extrusion. Holes can be cast in place to save additional machining
cost.
Stampings
Compared with stampings, one die casting can often replace several
parts. Die casting frequently require fewer assembly operations, can be
held within closer dimensional limits, can have almost any desired
variation in section thickness, involve less waste in scrap, and are
producible in more complex shapes. Die castings can be made in many
shapes not producible in stamped form.
Screw Machine Parts
Compared with screw machine products, die castings are produced more
rapidly, involve much less waste in scrap, can be made into shapes that are difficult or impossible to produce from bar or tubular stock, and may require fewer operations.
Sand castings
Compared with sand castings, die castings require much less
machining, can be made with thinner walls, can have all or nearly all holes cored to size, can be held within much closer dimensional limits, and are produced more rapidly in dies which make thousands of die castings without replacement. Die castings do not require new cores for each casting, are easily provided with inserts die cast in place, have smoother surfaces and involve much less labor cost per casting.
Permanent mold castings
Compared with permanent mold castings, die castings can be made to
closer dimensional limits and with thinner sections and holes can be
cored to near net shape. Die castings are produced at higher rates with
less manual labor, have smoother surfaces, and usually cost less per die casting.
Glossary of Die Casting Terms
Pictures and Photos of Die Casting Parts - End result of our efforts.
Die Casting Parts and Die Casting Processes:
California Die Casting Company. Tooling For Die Casting. Die Casting Part Draft Angle. Alloys for Die Casting. Aluminum Die Casting Company. Zinc Die Casting Company. Magnesium Die Casting Company. Porosity in Die Casting Parts. Sand Casting Prices and Die Casting Prices. Technical Information About Die Castings. Die Casting Parts Compared to Steel Parts. Die Casting Parts Compared to Plastic Parts. Kinetic Die Casting Company Limitations and Capabilities. Why Companies Use Die Casting Parts?. What is the Die Casting Process Description. American Die Casting Company . USA Manufacturing Company. Custom Metal Die Casting Parts. Diecast Quality Production. Die Casting Aluminum. Zinc Diecastings Parts. Kinetic Die Casting Company.
| Aluminum Die Casting Parts vs. Zinc Die Casting Parts: Key Differences |
|
Die casting is a high-pressure manufacturing process used to produce precise metal components with complex geometries. Aluminum and zinc are two of the most common alloys employed, but the resulting parts differ significantly due to their inherent material properties, casting … Continue reading |
| Kinetic Die Casting Wrap Up 2025 |
|
As we just completed another successful year of 2025 Kinetic Die Casting Company, we want to take a moment to thank you for your continued trust and collaboration. 2025 has been a year of growth, innovation, and resilience in the … Continue reading |
| Happy New Year 2026 from Kinetic Die Casting Company |
|
December 29, 2025 – Happy New Year – January 5, 2026, We will be back making great die casting parts for our customers. Kinetic Die Casting Company wishes to express our hope that your 2026 is a prosperous one. We … Continue reading |
| Kinetic Die Casting Company October 2025 |
|
Since 1994, Kinetic Die Casting Company sales@kineticdc.com has been making production parts using the die casting process. Normally, manufacturing companies that buy from die casting companies would simply lean towards the method of cold chamber aluminum die casting parts since … Continue reading |
| Die Casting Alloys 2025 |
|
Die Casting Aluminum Alloys are lightweight and possesses the stability to come up with thin walls and different shapes. This metal can resist corrosion and other mechanical properties. Moreover, it has excellent electrical and high thermal conductivity. Above all, aluminum … Continue reading |
| Die Casting Aluminum Heatsinks 2025 |
|
Die Casting Molds and Die Casting Procedures. Die casting aluminum Alloys is a process in which many industrial products and accessories are produced. And in producing these industrial products and accessories by way of die cast molds, four major steps … Continue reading |
| Get 500 Die Casting Parts Today |
|
Thank you for being our Kinetic Die Casting parts customer. Kinetic Die Casting Company makes parts for our manufacturing customers using the die casting process. What that means is, we inject molten metal into a steel die mold to make … Continue reading |
| Die Casting Parts Porosity |
|
Kinetic Die Casting Company sales@kineticdc.com is experienced in Solving Quality Problems of Porosity in Die Casting Parts. Porosity in die casting parts is an important issue in metal-working. Porosity, in the science of materials, refers to the presence of gaps … Continue reading |
| More die casting parts and the alloys used to make them |
|
Kinetic Die Casting Company specializes in making die casting parts, sales@kineticdc.com. When undergoing die casting, the type of metal alloy used determines the specific type of die casting that should be employed and the quality by which the die casting … Continue reading |
| Zinc Die Cast Knobs |
|
Zinc die-cast knobs are essential components in various industries, offering durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. With excellent strength and corrosion resistance properties, zinc die-cast knobs have become a popular choice for manufacturers due to their ability to withstand both indoor … Continue reading |
|
|
Site Map -
About -
Photos -
Technical -
Jobs -
Prices -
Home What? - Why - Our Abilities - Offshore ? - Sandcasting - Tooling - Newsletter |



